Concanavalin A Hepatitis plant lectin
Concanavalin A (Con A) is a plant lectin that is purified from jack beans. Con A binds to the mannose residues of varied glycoproteins and prompts lymphocytes. When Con A is run to mice, liver injury that can depend upon the activation of T lymphocytes by macrophages occurs (Tiegs et al., 1992). As a result of this reality, the model could allow the study of the pathophysiology of immunologically mediated hepatic points, resembling AIH. TNF-α and IFN-γ play important roles in Con A–induced liver injury (Gantner et al., 1995; Kusters et al., 1996) and IL-10 prevents liver injury on this model (Di Marco et al., 1999; Louis et al., 1997). Blood ranges of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-γ dramatically improve after administration of Con A (Wang et al., 2012). Essential drawbacks of this model embrace the dearth of circulating autoantibodies and quick hepatocyte damage following a single-dose Con A injection, which is not a typical attribute of persistent AIH.
Lectins as modulators of autophagy in most cancers immunotherapy
Concanavalin A prompts T cells and pure killer cells and triggers anticancer immune responses
Since ConA is a well-known T cell mitogen it would moreover set off anticancer immune responses by activating tumor specific CTLs. Actually, remedy of hepatoma-bearing mice (ML-14a cells) with ConA (7.5 mg/kg) strongly diminished liver tumor formation and prolonged survival, whereby 40% of the animals had been tumor free on the end of the experiment [8]. Lymphocytic infiltrates spherical tumor nodules had been seen in ConA-treated animals, suggesting T cell mediated responses. Actually, the depletion of CD8+ T cells completely abrogated the therapeutic outcomes of ConA, whereas the depletion of CD4+ T cells solely partly prevented ConA-mediated inhibition of tumor formation (Fig. 4A). In line with this study, ConA triggered CD4+ and CD8+ T cell activation in mice as confirmed by the upregulated expression of CD69 [74].
In addition to, ConA-treated mice contained elevated numbers of activated pure killer (NK) cells, T cells, and NK T cells, which confirmed sturdy cytotoxic train in opposition to murine lymphoma cells in ex vivo assays. That’s moreover translated proper right into a strongly diminished number of liver nodules upon ConA remedy of colon cancer-bearing mice (colon-26), an affect that was abrogated upon NK cell depletion (Fig. 4A). Of observe, NK cells in immunodeficient nude mice (lacking NKT and T cells) weren’t activated upon ConA remedy, suggesting a job of the adaptive immune system in activating NK cells [74].
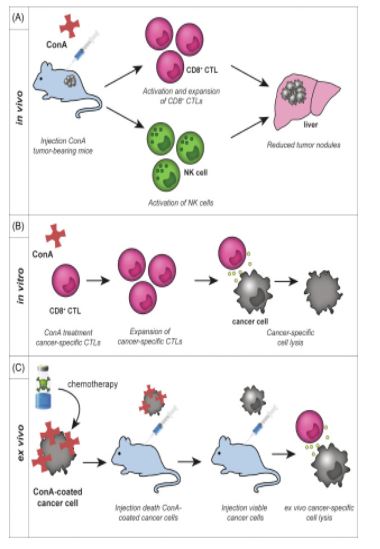
Furthermore, all outcomes had been abrogated in IFNγ knock-out mice, displaying the importance of an full of life immune response. Nonetheless, the remedy with ConA of hepatoma-bearing SCID mice moreover significantly inhibited liver tumor formation, nevertheless solely on the best dose of 20 mg/kg [8]. As SCID mice lack purposeful lymphocytes, these info counsel a direct cytotoxic affect of ConA in the direction of the most cancers cells. Actually, ConA induced direct autophagy-dependent cell demise in these mice (see above paragraph about ConA and most cancers cell demise). Thus, ConA prompts CD8+ CTLs and NK cells that in the reduction of in vivo tumor progress and potentiate ex vivo tumor cell lysis (Fig. 4A).
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Programmed cell death protein 10 (pdcd10) |
|||
| MBS1294649-01mgYeast | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(Yeast) | EUR 1035 |
) Recombinant Xenopus laevis Programmed cell death protein 10 (pdcd10) |
|||
| MBS1460047-002mgBaculovirus | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(Baculovirus) | EUR 1130 |
) Recombinant Xenopus laevis Programmed cell death protein 10 (pdcd10) |
|||
| MBS1460047-002mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(E-Coli) | EUR 715 |
) Recombinant Xenopus laevis Programmed cell death protein 10 (pdcd10) |
|||
| MBS1460047-002mgYeast | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(Yeast) | EUR 885 |
) Recombinant Xenopus laevis Programmed cell death protein 10 (pdcd10) |
|||
| MBS1460047-01mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(E-Coli) | EUR 860 |
) Recombinant Xenopus laevis Programmed cell death protein 10 (pdcd10) |
|||
| MBS1460047-01mgYeast | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(Yeast) | EUR 1035 |
, partial) Recombinant Xenopus laevis Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein (pdcd6ip), partial |
|||
| MBS1328223-INQUIRE | MyBiosource | INQUIRE | Ask for price |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Death-associated protein-like 1 (dapl1) |
|||
| MBS1392748-002mgBaculovirus | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(Baculovirus) | EUR 1035 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Death-associated protein-like 1 (dapl1) |
|||
| MBS1392748-002mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(E-Coli) | EUR 615 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Death-associated protein-like 1 (dapl1) |
|||
| MBS1392748-002mgYeast | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(Yeast) | EUR 790 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Death-associated protein-like 1 (dapl1) |
|||
| MBS1392748-01mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(E-Coli) | EUR 710 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Death-associated protein-like 1 (dapl1) |
|||
| MBS1392748-01mgYeast | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(Yeast) | EUR 925 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LBH (lbh) |
|||
| MBS1395853-002mgBaculovirus | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(Baculovirus) | EUR 1025 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LBH (lbh) |
|||
| MBS1395853-002mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(E-Coli) | EUR 600 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LBH (lbh) |
|||
| MBS1395853-002mgYeast | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(Yeast) | EUR 780 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LBH (lbh) |
|||
| MBS1395853-01mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(E-Coli) | EUR 695 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LBH (lbh) |
|||
| MBS1395853-01mgYeast | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(Yeast) | EUR 910 |
 Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 10 |
|||
| MBS1403715-002mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(E-Coli) | EUR 255 |
 Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 10 |
|||
| MBS1403715-01mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(E-Coli) | EUR 405 |
 Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 10 |
|||
| MBS1403715-1mgEColi | MyBiosource | 1mg(E-Coli) | EUR 1425 |
 Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 10 |
|||
| MBS1403715-5x1mgEColi | MyBiosource | 5x1mg(E-Coli) | EUR 6215 |
 Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 10 |
|||
| MBS9421374-002mg | MyBiosource | 0.02mg | EUR 285 |
 Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 10 |
|||
| MBS9421374-01mg | MyBiosource | 0.1mg | EUR 470 |
 Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 10 |
|||
| MBS9421374-1mg | MyBiosource | 1mg | EUR 1785 |
 Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 10 |
|||
| MBS9421374-5x1mg | MyBiosource | 5x1mg | EUR 7885 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LZIC (lzic) |
|||
| MBS1378725-002mgBaculovirus | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(Baculovirus) | EUR 1110 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LZIC (lzic) |
|||
| MBS1378725-002mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(E-Coli) | EUR 705 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LZIC (lzic) |
|||
| MBS1378725-002mgYeast | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(Yeast) | EUR 860 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LZIC (lzic) |
|||
| MBS1378725-01mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(E-Coli) | EUR 825 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein LZIC (lzic) |
|||
| MBS1378725-01mgYeast | MyBiosource | 0.1mg(Yeast) | EUR 1010 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein DPCD (dpcd) |
|||
| MBS1098104-002mgBaculovirus | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(Baculovirus) | EUR 1125 |
) Recombinant Xenopus tropicalis Protein DPCD (dpcd) |
|||
| MBS1098104-002mgEColi | MyBiosource | 0.02mg(E-Coli) | EUR 705 |