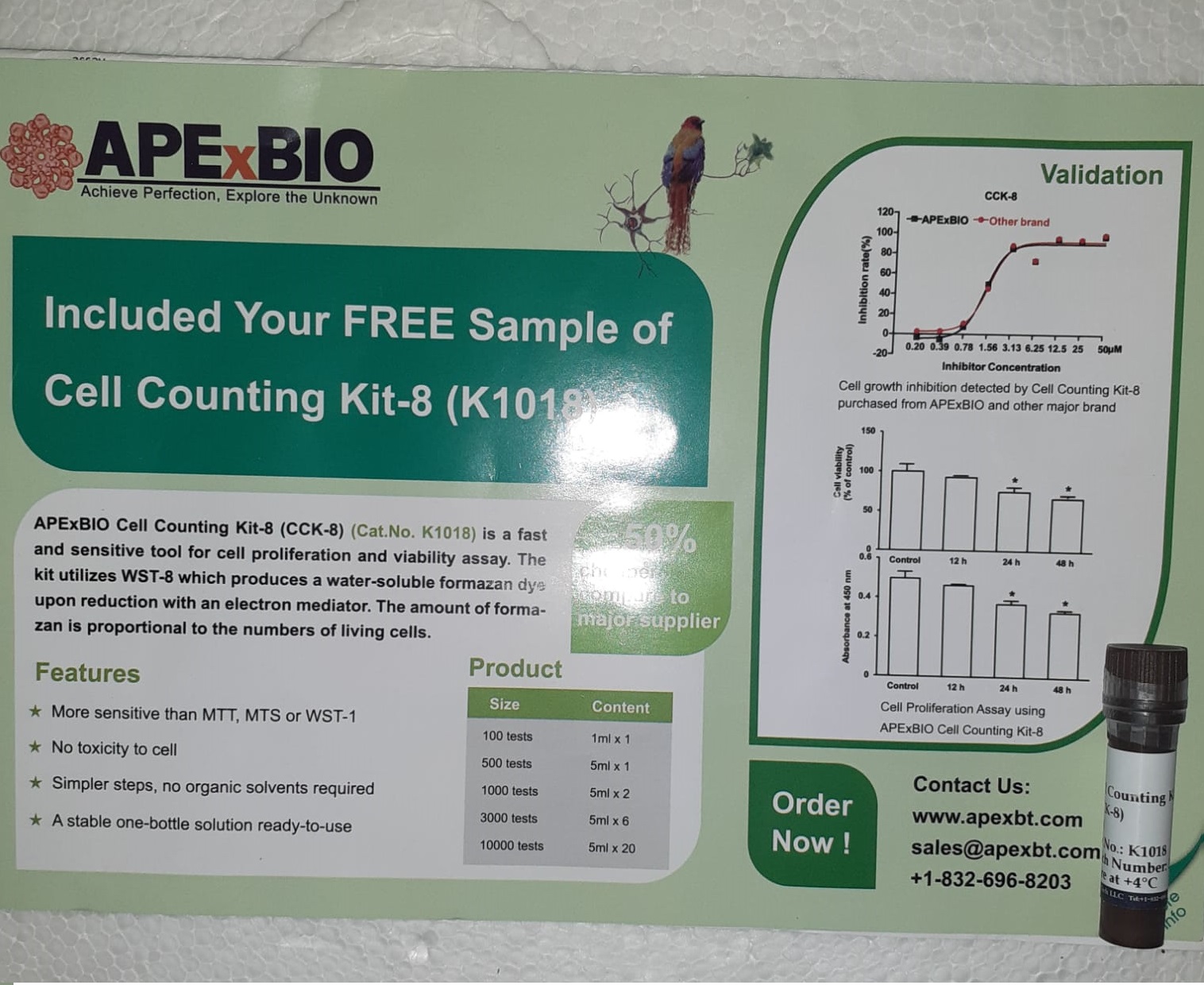
Propofol Affects Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cell Biology By Regulating the miR-21/PTEN/AKT Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo
Background: Propofol is a typical sedative-hypnotic drug historically used for inducing and sustaining basic anesthesia. Current research have drawn consideration to the nonanesthetic results of propofol, however the potential mechanism by which propofol suppresses non-small-cell lung most cancers (NSCLC) development has not been totally elucidated.
Strategies: For the in vitro experiments, we used propofol (0, 2, 5, and 10 µg/mL) to deal with A549 cells for 1, 4, and 12 hours and Cell Counting Package-8 (CCK-8) to detect proliferation. Apoptosis was measured with movement cytometry. We additionally transfected A549 cells with an microribonucleic acid-21 (miR-21) mimic or unfavorable management ribonucleic acid (RNA) duplex and phosphatase and tensin homolog, deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) or unfavorable management.
PTEN, phosphorylated protein kinase B (pAKT), and protein kinase B (AKT) expression have been detected utilizing Western blotting, whereas miR-21 expression was examined by real-time polymerase chain response (RT-PCR). In vivo, nude mice got injections of A549 cells to develop xenograft tumors; Eight days later, the mice have been intraperitoneally injected with propofol (35 mg/kg) or soybean oil. Tumors have been then collected from mice and analyzed by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting.
Outcomes: Propofol inhibited progress (1 hour, P = .001; Four hours, P ≤ .0001; 12 hours, P = .0004) and miR-21 expression (P ≤ .0001) and induced apoptosis (1 hour, P = .0022; Four hours, P = .0005; 12 hours, P ≤ .0001) in A549 cells in a time and concentration-dependent method.
MiR-21 mimic and PTEN siRNA transfection antagonized the suppressive results of propofol on A549 cells by reducing PTEN protein expression (imply variations [MD] [95% confidence interval {CI}], -0.51 [-0.86 to 0.16], P = .0058; MD [95% CI], 0.81 [0.07-1.55], P = .0349, respectively), leading to a rise in pAKT ranges (MD [95% CI] = -0.82 [-1.46 to -0.18], P = .0133) following propofol publicity. In vivo, propofol remedy diminished NSCLC tumor progress (MD [95% CI] = -109.47 [-167.03 to -51.91], P ≤ .0001) and promoted apoptosis (MD [95% CI] = 38.53 [11.69-65.36], P = .0093).
Conclusions: Our examine indicated that propofol inhibited A549 cell progress, accelerated apoptosis through the miR-21/PTEN/AKT pathway in vitro, suppressed NSCLC tumor cell progress, and promoted apoptosis in vivo. Our findings present new implications for propofol in most cancers remedy and point out that propofol is extraordinarily advantageous in surgical remedy.

Self-Organizing Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Hepatocyte 3D Organoids Inform the Biology of the Pleiotropic TRIB1 Gene
Institution of a physiologically related human hepatocyte-like cell system for in vitro translational analysis has been hampered by the restricted availability of cell fashions that precisely mirror human biology and the pathophysiology of human illness. Right here we report a strong, reproducible, and scalable protocol for the era of hepatic organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) utilizing brief publicity to nonengineered matrices.
These hepatic organoids observe outlined phases of hepatic growth and categorical greater ranges of early (hepatocyte nuclear issue 4A [HNF4A], prospero-related homeobox 1 [PROX1]) and mature hepatic and metabolic markers (albumin, asialoglycoprotein receptor 1 [ASGR1], CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α [C/EBPα]) than two-dimensional (2D) hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs) at day 20 of differentiation. We used this mannequin to discover the biology of the pleiotropic TRIB1 (Tribbles-1) gene related to various metabolic traits, together with nonalcoholic fatty liver illness and plasma lipids.
We used genome modifying to delete the TRIB1 gene in hiPSCs and in contrast TRIB1-deleted iPSC-HLCs to isogenic iPSC-HLCs underneath each 2D tradition and three-dimensional (3D) organoid situations. Beneath standard 2D tradition situations, TRIB1-deficient HLCs confirmed maturation defects, with decreased expression of late-stage hepatic and lipogenesis markers.
In distinction, when cultured as 3D hepatic organoids, the differentiation defects have been rescued, and a transparent lipid-related phenotype was famous within the TRIB1-deficient induced pluripotent stem cell HLCs. Conclusion: This work helps the potential of genome-edited hiPSC-derived hepatic 3D organoids in exploring human hepatocyte biology, together with the useful interrogation of genes recognized via human genetic investigation.
Offered here’s a genome sequence of a person human. It was produced from roughly 32 million random DNA fragments, sequenced by Sanger dideoxy know-how and assembled into 4,528 scaffolds, comprising 2,810 million bases (Mb) of contiguous sequence with roughly 7.5-fold protection for any given area.
We developed a modified model of the Celera assembler to facilitate the identification and comparability of alternate alleles inside this particular person diploid genome. Comparability of this genome and the Nationwide Middle for Biotechnology Info human reference meeting revealed greater than 4.1 million DNA variants, encompassing 12.Three Mb.
These variants (of which 1,288,319 have been novel) included 3,213,401 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), 53,823 block substitutions (2-206 bp), 292,102 heterozygous insertion/deletion occasions (indels)(1-571 bp), 559,473 homozygous indels (1-82,711 bp), 90 inversions, in addition to quite a few segmental duplications and replica quantity variation areas. Non-SNP DNA variation accounts for 22% of all occasions recognized within the donor, nonetheless they contain 74% of all variant bases.
This means an necessary function for non-SNP genetic alterations in defining the diploid genome construction. Furthermore, 44% of genes have been heterozygous for a number of variants. Utilizing a novel haplotype meeting technique, we have been capable of span 1.5 Gb of genome sequence in segments >200 kb, offering additional precision to the diploid nature of the genome. These information depict a definitive molecular portrait of a diploid human genome that gives a place to begin for future genome comparisons and allows an period of individualized genomic info.
Elementary options of microbial cellulose utilization are examined at successively greater ranges of aggregation encompassing the construction and composition of cellulosic biomass, taxonomic range, cellulase enzyme programs, molecular biology of cellulase enzymes, physiology of cellulolytic microorganisms, ecological facets of cellulase-degrading communities, and rate-limiting components in nature.
The methodological foundation for learning microbial cellulose utilization is taken into account relative to quantification of cells and enzymes within the presence of stable substrates in addition to equipment and evaluation for cellulose-grown steady cultures. Quantitative description of cellulose hydrolysis is addressed with respect to adsorption of cellulase enzymes, charges of enzymatic hydrolysis, bioenergetics of microbial cellulose utilization, kinetics of microbial cellulose utilization, and contrasting options in comparison with soluble substrate kinetics.
A organic perspective on processing cellulosic biomass is offered, together with options of pretreated substrates and different course of configurations. Organism growth is taken into account for “consolidated bioprocessing” (CBP), wherein the manufacturing of cellulolytic enzymes, hydrolysis of biomass, and fermentation of ensuing sugars to desired merchandise happen in a single step.
Two organism growth methods for CBP are examined: (i) enhance product yield and tolerance in microorganisms capable of make the most of cellulose, or (ii) categorical a heterologous system for cellulose hydrolysis and utilization in microorganisms that exhibit excessive product yield and tolerance. A concluding dialogue identifies unresolved points pertaining to microbial cellulose utilization, suggests approaches by which such points could be resolved, and contrasts a microbially oriented cellulose hydrolysis paradigm to the extra standard enzymatically oriented paradigm in each basic and utilized contexts.
 AAV3-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-303 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: GFP control virus of AAV serotype 3. |
|||
 AAV4-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-304 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: GFP control virus of AAV serotype 4. |
|||
 AAV5-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-305 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: GFP control virus of AAV serotype 5. |
|||
 AAV6-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-306 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: GFP control virus of AAV serotype 6. |
|||
 AAV2 Null Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-352 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Null (empty) control virus of AAV serotype 2. |
|||
 AAV3 Null Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-353 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Null (empty) control virus of AAV serotype 3. |
|||
 AAV4 Null Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-354 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Null (empty) control virus of AAV serotype 4. |
|||
 AAV5 Null Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-355 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Null (empty) control virus of AAV serotype 5. |
|||
 AAV6 Null Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-356 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Null (empty) control virus of AAV serotype 6. |
|||
 AAV2-Cre Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-310 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Cre control virus of AAV serotype 2. |
|||
 AAV3-Cre Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-313 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Cre control virus of AAV serotype 3. |
|||
 AAV4-Cre Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-314 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Cre control virus of AAV serotype 4. |
|||
 AAV5-Cre Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-315 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Cre control virus of AAV serotype 5. |
|||
 AAV6-Cre Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-316 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Cre control virus of AAV serotype 6. |
|||
 AAV2-Luc Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-320 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Luciferase control virus of AAV serotype 2. |
|||
 AAV3-Luc Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-323 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Luciferase control virus of AAV serotype 3. |
|||
 AAV4-Luc Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-324 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Luciferase control virus of AAV serotype 4. |
|||
 AAV5-Luc Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-325 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Luciferase control virus of AAV serotype 5. |
|||
 AAV6-Luc Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-326 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Luciferase control virus of AAV serotype 6. |
|||
 AAV2-LacZ Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-342 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: LacZ control virus of AAV serotype 2. |
|||
 AAV3-LacZ Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-343 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: LacZ control virus of AAV serotype 3. |
|||
 AAV4-LacZ Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-344 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: LacZ control virus of AAV serotype 4. |
|||
 AAV5-LacZ Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-345 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: LacZ control virus of AAV serotype 5. |
|||
 AAV6-LacZ Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-346 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: LacZ control virus of AAV serotype 6. |
|||
) saCas9 Nuclease AAV Virus (AAV1) |
|||
| K208 | ABM | 2 x 250 µl, 1 x 10^9 GC/ml, Titer: 1 x 10^9 GC/ml | EUR 375 |
|
Description: This AAV vector expresses the Cas9 orthologue from Staphylococcus Aureus (saCas9). saCas9 is ~1 kb shorter than spCas9, allowing it to be efficiently packaged in AAV Virus. Furthermore, the saCas9 enzyme recognizes a longer PAM sequence than spCas9, and thus has greater editing specificity.AAV has low immunogenicity and broad host range, making it an ideal choice for both in vivo and in vitro applications. Use this saCas9-expressing AAV virus with a target-specific saCas9-compatible sgRNA for highly specific and efficient genome editing. |
|||
 scAAV1-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-331 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Self-complementary GFP control virus of AAV serotype 1. |
|||
 scAAV2-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-332 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Self-complementary GFP control virus of AAV serotype 2. |
|||
 scAAV3-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-333 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Self-complementary GFP control virus of AAV serotype 3. |
|||
 scAAV4-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-334 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Self-complementary GFP control virus of AAV serotype 4. |
|||
 scAAV5-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-335 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Self-complementary GFP control virus of AAV serotype 5. |
|||
 scAAV6-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| AAV-336 | Cell Biolabs | 50 ?L | EUR 1221.6 |
|
Description: Self-complementary GFP control virus of AAV serotype 6. |
|||
 Lenti-III-UBC-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| LV027 | ABM | 4 x 500 ul | EUR 195 |
 Lenti-III-PGK-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| LV028 | ABM | 4 x 500 ul | EUR 195 |
 Lenti-III-EF1alpha-GFP Control Virus |
|||
| LV046 | ABM | 4 x 500 ul | EUR 195 |
 ELISA Kit) Human Adeno Associated Virus Type 1 (AAV1) ELISA Kit |
|||
| MBS9376028-10x96StripWells | MyBiosource | 10x96-Strip-Wells | EUR 6725 |
 ELISA Kit) Human Adeno Associated Virus Type 1 (AAV1) ELISA Kit |
|||
| MBS9376028-48StripWells | MyBiosource | 48-Strip-Wells | EUR 550 |
 ELISA Kit) Human Adeno Associated Virus Type 1 (AAV1) ELISA Kit |
|||
| MBS9376028-5x96StripWells | MyBiosource | 5x96-Strip-Wells | EUR 3420 |
 ELISA Kit) Human Adeno Associated Virus Type 1 (AAV1) ELISA Kit |
|||
| MBS9376028-96StripWells | MyBiosource | 96-Strip-Wells | EUR 765 |
) pCDH-Cuo-RFP-T2A-GFP (positive control virus) |
|||
| QM350VA-1 | SBI | >1 x 10^6 IFUs | EUR 573 |
 KRV Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412091-1mL | MyBiosource | 1mL | EUR 175 |
 KRV Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412091-5x1mL | MyBiosource | 5x1mL | EUR 645 |
 Zika Virus Negative Control |
|||
| MBS412678-05mL | MyBiosource | 0.5mL | EUR 100 |
 Zika Virus Negative Control |
|||
| MBS412678-5x05mL | MyBiosource | 5x0.5mL | EUR 305 |
 Zika Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412728-05mL | MyBiosource | 0.5mL | EUR 195 |
 Zika Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412728-5x05mL | MyBiosource | 5x0.5mL | EUR 730 |
 Foamy Virus Negative Control |
|||
| MBS412663-05mL | MyBiosource | 0.5mL | EUR 100 |
 Foamy Virus Negative Control |
|||
| MBS412663-5x05mL | MyBiosource | 5x0.5mL | EUR 305 |
 Foamy Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412713-05mL | MyBiosource | 0.5mL | EUR 195 |
 Foamy Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412713-5x05mL | MyBiosource | 5x0.5mL | EUR 730 |
 HSV-1 Virus Control Stock |
|||
| 20-4810020 | Quidel | Single Use, 400 µL, shipped frozen | Ask for price |
|
Description: Genetically Engineered BHK Cells |
|||
 HSV-2 Virus Control Stock |
|||
| 20-4820020 | Quidel | Single Use, 400 µL, shipped frozen | Ask for price |
|
Description: Genetically Engineered BHK Cells |
|||
 Zika Virus NS1 Control Antigen |
|||
| BA149R01 | Genovis AB | 1 mg | EUR 947 |
 Rubella Virus IgG Control Serum |
|||
| C129G | Genovis AB | 3 mL | EUR 105 |
 Rubella Virus IgM Control Serum |
|||
| C129M | Genovis AB | 3 mL | EUR 105 |
 Measles Virus IgG Control Serum |
|||
| C102G | Genovis AB | 3 mL | EUR 105 |
 Measles Virus IgM Control Serum |
|||
| C102M | Genovis AB | 3 mL | EUR 105 |
 Zika Virus NS5 Positive Control |
|||
| MBS543408-5Applications | MyBiosource | 5Applications | EUR 335 |
 Zika Virus NS5 Positive Control |
|||
| MBS543408-5x5Applications | MyBiosource | 5x5Applications | EUR 1350 |
 Zika Virus NS1 Positive Control |
|||
| MBS5400765-5Applications | MyBiosource | 5Applications | EUR 335 |
 Zika Virus NS1 Positive Control |
|||
| MBS5400765-5x5Applications | MyBiosource | 5x5Applications | EUR 1350 |
 Zika Virus NS2 Positive Control |
|||
| MBS5400766-5Applications | MyBiosource | 5Applications | EUR 335 |
 Zika Virus NS2 Positive Control |
|||
| MBS5400766-5x5Applications | MyBiosource | 5x5Applications | EUR 1350 |
 Zika Virus NS3 Positive Control |
|||
| MBS5400767-5Applications | MyBiosource | 5Applications | EUR 335 |
 Zika Virus NS3 Positive Control |
|||
| MBS5400767-5x5Applications | MyBiosource | 5x5Applications | EUR 1350 |
 Mouse K Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412089-1mL | MyBiosource | 1mL | EUR 195 |
 Mouse K Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412089-5x1mL | MyBiosource | 5x1mL | EUR 720 |
 Lenti-III-PGK-Luc Control Virus |
|||
| LV088 | ABM | 4 x 500 ul | EUR 195 |
 Control) Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Control |
|||
| MBS568624-1mL | MyBiosource | 1mL | EUR 300 |
 Control) Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Control |
|||
| MBS568624-25mL | MyBiosource | 25mL | EUR 2830 |
 Control) Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Control |
|||
| MBS568624-5x25mL | MyBiosource | 5x25mL | EUR 12475 |
 Rat Hanta Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412088-1mL | MyBiosource | 1mL | EUR 175 |
 Rat Hanta Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412088-5x1mL | MyBiosource | 5x1mL | EUR 645 |
 West Nile Virus Negative Control |
|||
| MBS412656-05mL | MyBiosource | 0.5mL | EUR 100 |
 West Nile Virus Negative Control |
|||
| MBS412656-5x05mL | MyBiosource | 5x0.5mL | EUR 305 |
 West Nile Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412706-05mL | MyBiosource | 0.5mL | EUR 195 |
 West Nile Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412706-5x05mL | MyBiosource | 5x0.5mL | EUR 730 |
 Mouse Zika Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412086-05mL | MyBiosource | 0.5mL | EUR 175 |
 Mouse Zika Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412086-5x05mL | MyBiosource | 5x0.5mL | EUR 645 |
 Rat Sendai Virus Positive Control |
|||
| MBS412130-1mL | MyBiosource | 1mL | EUR 175 |